TCP/IP:-इस Protocol समूह से Modern Communication कर सकते हैं इसमें केबल 4 Layers होती हैं ।
1-Application 2-Transport 3-Internet 4-Network
Socket:-Tcp Protocol में Port का प्रयोग होता है और Port Number और IP मिलकर एक Socket बनाते है ।
IP-10.10.10.29
Port-23
Socket-10.10.10.10.29:23
Check the Protocol Port
Network Card+Properties+Sharing+Setting.
PAP:-(Password Authentication Protocol)
ये Authentication का कमजोर Method है इस में password और user name Plain text पर जाता है ।
CHAP:-(Chalange Hands Shakeauthentication Protocol)
ये Security का Strong Protocol है इसमे यूजर और password Incripted Chipher text form में जाता है ।
TCP:-(Transmission Control Protoco) TCP Protocol Connection Oriented होता है ।
IM:-(Instant messaging) ये E-mail से थोड़ी Difrent Service है ये smg की Delebry तुरंत देती है । इसमे XMPP , OSCAR ये IRC पर Basic होता है ।
XMPP:-Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol
OSCAR:-Open System for Communication in Realtime
IRC:-Internet Relay Chat
Example:-Fb Chat , gtalk , vtalk , jabbar , ATM.
UDP:-(User Data Gram Protocol) ये Connection Less Protocol है । इसकी Transfer Speed Tcp की अपेछा Fast होती है । लेकिन यह Data की कोई गारंटी नहीं लेता ।
ICMP:-(Internet Control Massage Protocol) यह Data massage को Control करता है यह Error Reporting Data है । Ping इसके दुयारा ही जाता है ।
ARP:-(Address Resulution Protocol) इस Protocol की Help से IP Address को Mac Address में Divice को Map करते है ।
RARP:-(Revirs Address Resolution Protocol) इस Protocol की Help से Mac Address को IP Address में Convert करते है । Mac Address 48 -bit का होता है ।
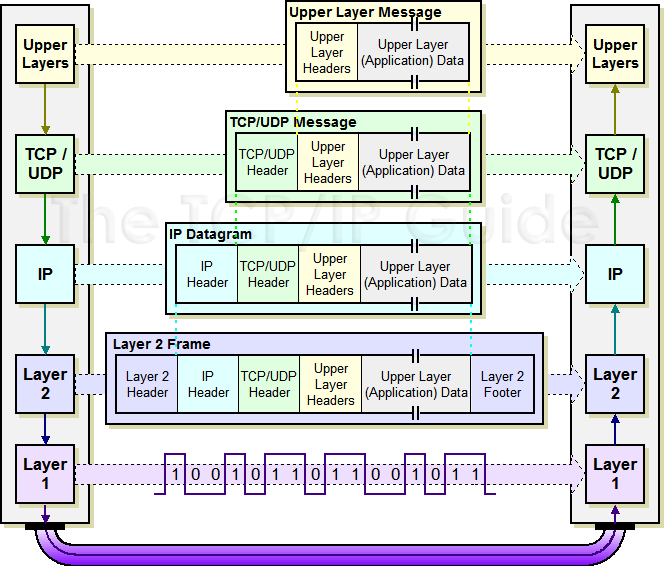
Encapsulation:-Data bits का Fream और Fream का Packets में Convert होना । OSI Model और TCP /IP Model में Data Packed का Upper layer तक जाना Encapsulation कहलाता है ।
Example:-Fb Chat , gtalk , vtalk , jabbar , ATM.
UDP:-(User Data Gram Protocol) ये Connection Less Protocol है । इसकी Transfer Speed Tcp की अपेछा Fast होती है । लेकिन यह Data की कोई गारंटी नहीं लेता ।
ICMP:-(Internet Control Massage Protocol) यह Data massage को Control करता है यह Error Reporting Data है । Ping इसके दुयारा ही जाता है ।
ARP:-(Address Resulution Protocol) इस Protocol की Help से IP Address को Mac Address में Divice को Map करते है ।
RARP:-(Revirs Address Resolution Protocol) इस Protocol की Help से Mac Address को IP Address में Convert करते है । Mac Address 48 -bit का होता है ।
Encapsulation:-Data bits का Fream और Fream का Packets में Convert होना । OSI Model और TCP /IP Model में Data Packed का Upper layer तक जाना Encapsulation कहलाता है ।
IP Addressing :-इस के 5 Class होते है ।
Class A 1-126
Class B 128-191
Class C 192-223
Class D 224-239
Class E 240-255
| Class | Leftmost bits | Start address | Finish address |
| A | 0xxx | 0.0.0.0 | 127.255.255.255 |
| B | 10xx | 128.0.0.0 | 191.255.255.255 |
| C | 110x | 192.0.0.0 | 223.255.255.255 |
| D | 1110 | 224.0.0.0 | 239.255.255.255 |
| E | 1111 | 240.0.0.0 | 255.255.255.255 |
Note:Class D,E का use Scientifle Lab में होता है । Class A में आगे की 8 Bit Network कि और पीछे Host की होती है ।
n.n.nnnnnn.hhhhhhhh.h.h
Network 8Host 8h 8h
8Network 24Host
Class B की 16 BIT आगे और Network 16 BIT पीछे Host
Class C की 24 BIT आगे और Network 8 BIT पीछे Host
IP Address Class
|
Total # Of Bits For Network ID / Host ID
|
First Octet of IP Address
|
# Of Network ID Bits Used To Identify Class
|
Usable # Of Network ID Bits
|
Number of Possible Network IDs
|
# Of Host IDs Per Network ID
|
Class A
|
8 / 24
|
0xxx xxxx
|
1
|
8-1 = 7
|
27-2 = 126
|
224-2 = 16,277,214
|
Class B
|
16 / 16
|
10xx xxxx
|
2
|
16-2 = 14
|
214 = 16,384
|
216-2 = 65,534
|
Class C
|
24 / 8
|
110x xxxx
|
3
|
24-3 = 21
|
221 = 2,097,152
|
28-2 = 254
|
IP address classes
| Class | 1st Octet Decimal Range | 1st Octet High Order Bits | Network/Host ID (N=Network, H=Host) | Default Subnet Mask | Number of Networks | Hosts per Network (Usable Addresses) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1 – 126* | 0 | N.H.H.H | 255.0.0.0 | 126 (27 – 2) | 16,777,214 (224 – 2) |
| B | 128 – 191 | 10 | N.N.H.H | 255.255.0.0 | 16,382 (214 – 2) | 65,534 (216 – 2) |
| C | 192 – 223 | 110 | N.N.N.H | 255.255.255.0 | 2,097,150 (221 – 2) | 254 (28 – 2) |
| D | 224 – 239 | 1110 | Reserved for Multicasting | |||
| E | 240 – 254 | 1111 | Experimental; used for research | |||
Note: Class A addresses 127.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255 cannot be used and is reserved for loopback and diagnostic functions.
Private IP Addresses
| Class | Private Networks | Subnet Mask | Address Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 10.0.0.0 | 255.0.0.0 | 10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255 |
| B | 172.16.0.0 - 172.31.0.0 | 255.240.0.0 | 172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255 |
| C | 192.168.0.0 | 255.255.0.0 | 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 |
OSI Model
| Layer # | Name | Mnemonic | Encapsulation Units | Devices or Components | Keywords/Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | Application | All | data | PC | Network services for application processes, such as file, print, messaging, database services |
| 6 | Presentation | People | data | Standard interface to data for the application layer. MIME encoding, data encryption, conversion, formatting, compression | |
| 5 | Session | Seem | data | Interhost communication. Establishes, manages and terminates connection between applications | |
| 4 | Transport | To | segments | End-to-end connections and reliability. Segmentation/desegmentation of data in proper sequence. Flow control | |
| 3 | Network | Need | packets | router | Logical addressing and path determination. Routing. Reporting delivery errors |
| 2 | Data Link | Data | frames | bridge, switch, NIC | Physical addressing and access to media. Two sublayers: Logical Link Control (LLC) and Media Access Control (MAC) |
| 1 | Physical | Processing | bits | repeater, hub, transciever | Binary transmission signals and encoding. Layout of pins, voltages, cable specifications, modulation |
OSI comparision with TCP/IP Protocol Stack
| OSI # | OSI Layer Name | TCP/IP # | TCP/IP Layer Name | Encapsulation Units | TCP/IP Protocols |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | Application | 4 | Application | data | FTP, HTTP, POP3, IMAP, telnet, SMTP, DNS, TFTP |
| 6 | Presentation | data | |||
| 5 | Session | data | |||
| 4 | Transport | 3 | Transport | segments | TCP, UDP |
| 3 | Network | 2 | Internet | packets | IP |
| 2 | Data Link | 1 | Network Access | frames | |
| 1 | Physical | bits |






0 comments:
Post a Comment